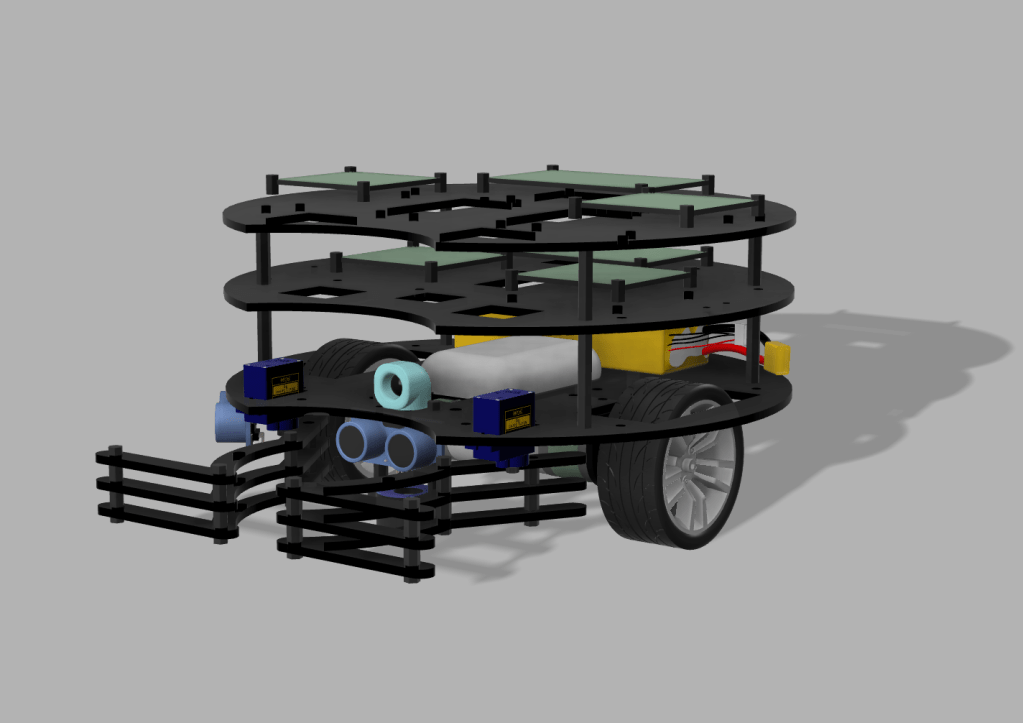
This project entails the development of a mobile autonomous robot with advanced sensing and communication capabilities. The robot exhibits autonomous wall-following behavior, precise localization through Vive system integration, and employs infrared beacon tracking for targeted navigation. Notably, it communicates using communication protocols such as UDP and ESPNow, enabling dynamic interaction. The robot’s proficiency is demonstrated by its ability to autonomously manipulate objects, including grabbing a real trophy, pushing a fake trophy and a police car with precision, highlighting its adaptability in practical applications.
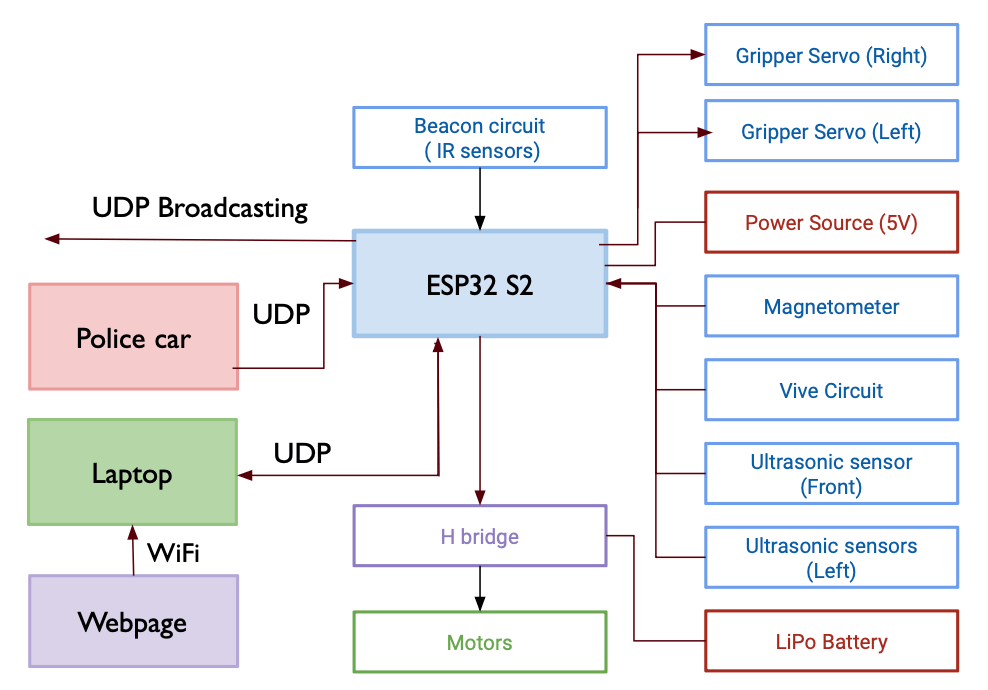
Key features: Sensing and Perception: In the sensor domain, the robot integrated infrared sensors with carefully crafted detection circuits and ultrasonic sensors with software filters. This robust sensing foundation was seamlessly integrated into the robot’s navigation and task-specific functionalities.
Localization System: The robot employed the HTC Vive, a GPS-like localization system, to precisely determine its position within the environment. Calibration ensured accurate alignment between the Vive system and the robot’s internal coordinate system, and a magnetometer provided relative orientation information for a comprehensive localization system.
Planning and Obstacle Avoidance: The planning strategy used the start position from Vive localization and the end goal defined by either IR frequency recognition or Vive coordinates. A simplified path planning approach prioritized ease of control, and reactive obstacle avoidance mechanisms using sensor inputs ensured efficient maneuvering through the designated field.
Control Strategy and Web Interface Design: The control strategy implemented PID controllers for lateral and longitudinal control, guiding the robot’s movements based on planning module input. A web interface hosted on an HTML-based webpage allowed interaction with the robot through UDP WiFi communication. ESPNOW communication is also used to send messages to the other robots. The interface featured task selection options, a stop button, and flags for task completion or timeout.