The go-kart mechatronics system is designed as a modular system, consisting of several subsystems that are responsible for different tasks. There are seven major subsystems:
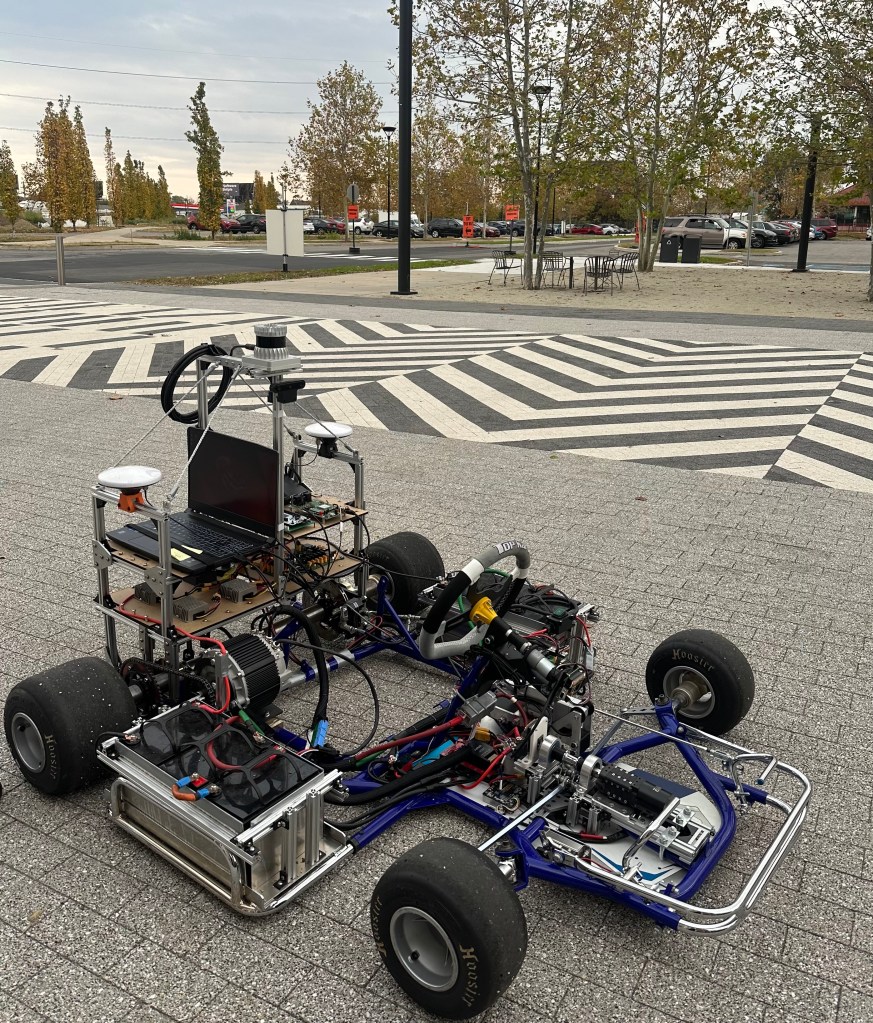

The “x-by-wire” system design approach has been gaining popularity in the automotive industry which is to replace conventional mechanical and hydraulic control systems with electronic signals. The elimination of traditional mechanical components could increase control stability, in- crease design flexibility, reduce cost, and improve efficiency . In our go-kart drive-by-wire design, all subsystems except the PD and the RSD use an STM32 Nucleo development board on a standalone PCB as the electronic control unit (ECU). Like modern vehicle design, communication is achieved using the controller area network (CAN) to allow efficient information exchange between nodes . These modular control systems are integrated with the original go-kart chassis in a non-intrusive manner and are easy to understand, build, and modify.
Cone SLAM:
After employing YOLOv8 transfer learning on the FSOCO Dataset for cone detection, the subsequent step involves determining the positions of the detected cones within the scene. Utilizing the output from the YOLOv8 model, which accurately identifies cones in various environmental conditions, I analyzed the spatial coordinates and dimensions of the detected cones to ascertain their precise locations. This process entails mapping the detected cones onto a coordinate system relative to the camera or robot’s position, enabling real-time tracking and navigation around the identified obstacles. By accurately determining the positions of cones, derived from the refined YOLOv8 model trained on the FSOCO Dataset, I am working to facilitate enhanced navigation and path planning algorithms, crucial for autonomous systems operating in dynamic environments.


Visual SLAM:
Using the RealSense camera, I am leveraging image sequences to map environments and estimating robot trajectories in real-time, to enhance localization accuracy. By integrating visual sensor data with wheel odometer, Visual SLAM enables autonomous systems to navigate complex environments with precision and efficiency.